Printed around the border or margin of the map are the information and additional facts about the specific map sheet that a given user is reading. This is referred to as Marginal Information. They are the basic components of a map since they give supportive details to make a map well defined and understood.
Marginal information found in topographic maps include the following;
1. Map Title (or Map Sheet Name)
Map title is the name or heading of the particular map sheet. It is usually printed in bold letters on the top of the map sheet. Usually, a map sheet is named after its most prominent cultural feature e.g. largest settlement and important town, or the largest natural physical feature on the map like a mountain, lake, forest or crater. Sometimes, map sheet titles can also indicate the information that the map user is expected to find on the map.
2. Map Identification
Map identification refers the information about the identity of a particular map sheet. This information is useful to anyone intending to use or purchase a similar map. Thus, if one quotes this information, it will be easy for the survey department personnel to find the required map sheet. Map identification consists of three elements which are usually used when identifying any map sheet. These are the map series number, the map sheet number, and the edition designation.
·
Map Series Number
A map series refers to a group of maps
having the same scale and cartographic specifications designed to cover a
particular geographic area. It may also be a group of maps that serve a common
purpose, such as the military city maps.
Map series number is a reference number
that is used to identify a given map series. All map sheets in a given map
series share the same map series number. It is usually expressed either as a
four-digit numeral (1034) or as a letter, followed by a three- or four-digit
numeral (Y321; T7110).
·
Map Sheet Number
Map sheet number is a reference number that
distinguishes one map from other maps in the same map series. Each map sheet has its own map sheet number. The
map sheet number is usually shown in the upper right corner of the margin. It can
also be seen in the center box of the adjoining sheets diagram, which is found
in the lower right margin of the map.
·
Edition Designation
Edition designation gives information about
the publication of the map. It is a specific identification based on the
publication sequence of a particular map. Edition designation is useful when
identifying the up-to-dateness of the information shown on the map.
Edition designation consists of three parts;
the edition number; the name of the agency responsible for producing of the map
and the year the map was published. Example: Edition 4-AMS 1984.
The edition
numbers run consecutively i.e. They increase at each revision. Thus, a map
labeled with a higher edition number contains more recent information than the
one with a lower edition number. The letters following the edition number
indicate the abbreviation of the agency which produced the map. Some of the
common agencies include; geographical section general staff (GSGS), united
states geological survey (USGS) and directorate of overseas surveys (DOS). The year
on the edition designation indicates the time the map was published and it is
important when determining how accurately the map data might be expected to
match what you will encounter on the ground.
All the information about map identification is usually
enclosed in a box or placed together in a panel as shown below
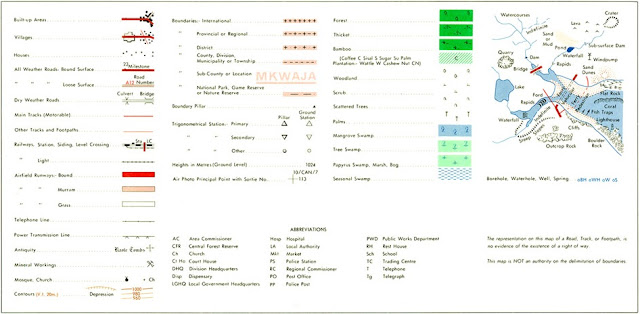
3. Legend
A legend (also known as a key) is a table which explains the
meanings of the conventional symbols, colors, and abbreviations used on a
corresponding map. A legend consists of each symbol shown on the map, with a
short description of its meaning. However, it should be noted that the legend
simply includes information of all maps on a given map series. Thus, not all
information contained in the legend will be found on the map.
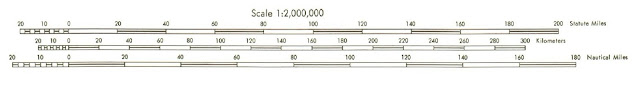
4. Scale
To create an accurate picture of the landscape on paper,
everything has to be made much, much smaller. This is done by scaling down the
actual size of the land. The amount by which the actual size of the earth’s
surface has been reduced down in order for the map to be drawn is known as the
scale of a map. The scale of a map basically gives the ratio between the
distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the earth’s surface.
On the map, scale is usually represented in two ways; as a
ratio scale and as a linear scale.
For the example below, the ratio scale is 1:500,000. What
this means is that one unit on the map represents 500,000 same units on the
ground. On the map sheet, the ratio scale can be found in the upper left margin
after the map sheet name, and in the lower margin of the map sheet.
And just below the ratio scale, is the linear scale or sometimes called the bar
scale. A linear scale is usually in form of a horizontal bar and it can be used
to make fast estimates of distance on the map.
5. Map Borders
A map border is a framework of the map understudy. It identifies
exactly where the mapped area ends. Most of the topographic maps usually have
two borders; the neatline and the borderline. The neatline only encloses the
mapped area, while the borderline encloses both the neatline and mapped
area. The borderlines are usually
thicker than the neatlines.
Maps may have only one border, but cartographers prefer to
use both the borderline and the neatline to make a map more visually appealing.
Usually, the distance between the borderline and the neatline is always the
same on all sides of the map.
6.. Index to Adjoining Sheets /Adjoining Sheets Diagram
In the margins of most topographic maps, there is usually a
box containing 9 squares whereby the central square (usually shaded) represents
the map that is being used at the moment. The other squares represent the maps
surrounding the map sheet being used. This box is what is referred to as the
index to adjoining sheets diagram. The index to adjoining sheets diagram
provides information of the neighboring map sheets by showing the sheet number
and names of the neighboring sheets. The information in the index to adjoining
sheets diagram is important to a map user in case he/she needs to purchase or
refer to a particular map in the series.
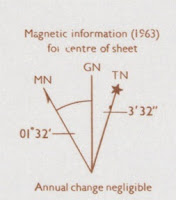
7. Declination Diagram
Early maps almost always had an arrow indicating to the
direction of the geographic north pole-called the north arrow. By showing the
north direction, it is easy for the map user to identify other important
directions like west, east and south
However, in modern topographic maps, the information
regarding the direction of north is given in the form of a diagram known as the
declination diagram. This diagram is usually located in the lower margin of the
map sheet
The declination diagram shows the angular relationship
between the three types of north: true north, magnetic north, and grid
north. The information presented in this
diagram relates directly to the orientation of true north, magnetic and grid
north; and the magnetic declination of the mapped area, as calculated from the
center of the map sheet in the survey year indicated.
The year in which the
magnetic declination was measured and the annual rate of change of the
declination is also stated in this diagram
Ø
True north or geographic
north is the direction towards the North Pole from any place on the earth’s
surface. On the declination diagram, the line of true north is shown with a
star on top.
Ø Magnetic north is the
direction determined by a magnetic compass needle. The magnetic compass needle
usually points towards the magnetic north pole. On
the declination diagram, a magnetic north line is usually shown with half an
arrowhead on top.
Ø
Grid north is the
direction shown by the vertical grid lines on maps drawn using UTM grid system.
Grid north is useful because it allows you to use UTM grid lines on your map as
the north reference. Unlike true and magnetic north, the line of grid north is
usually bare on the declination diagram
Ø
Magnetic declination is
the angle that lies in between the true north line and the magnetic north line.
8. Name of Publisher and Copyright
Owner of the Map
Topographic maps are accurately drawn and published by a
given authority. The department for surveys of each country is usually in
charge of producing maps after carrying out the required survey. It may also do
this with the assistance of overseas organizations such as the ‘Directorate of Overseas Survey (D.O.S) of England. A large number of topographic maps have
been produced by D.O.S in England on behalf of African governments. However,
the permission for reproducing the map extracts can only be given by the
copyright owner. In most cases, the
government of the country concerned is the copyright owner of the given map
extract.
It is important for the name of the publisher whether (individual
cartographer or an institution) and the copyright owner to appear on the map
sheet. This may help the map users to make necessary consultation with the
cartographer to have clarification on details about the area which has been
mapped or request for the permission of reproducing the map from the copyright
owner of the map.
9. Index To Boundaries Diagram
The index to boundaries diagram, which is a miniature of the
map, shows the administrative boundaries that occur within the mapped area. It
enables a map user to identify the administrative units such as in states,
provinces, counties, cities, and towns; that appear on the main map.
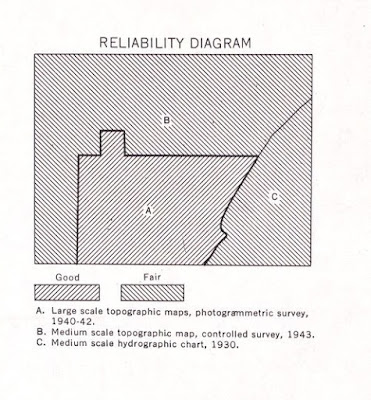
10. Reliability Diagram
When a map has been compiled from several sources, a
reliability diagram may be provided in the bottom margin of the map sheet to
show the extent of coverage of the basic sources for different parts of the
sheet.
The reliability diagram contains graphic references to the
reliability of the sources used and indicates the methods by which the map was
made, dates of photography, and r the degree of reliability of different parts
of the sheet
This diagram will be found on maps only when the reliability
of the information compiled is below the standard which is normally expected at
that scale and in that area.
If you need to know
the definition of any geographic term, word, or vocabulary found in this post,
click here to be redirected to the Glossary of this blog.










Good work thanks 👍
ReplyDeleteSO NICE
DeleteNice work ..usefull
ReplyDeleteVery nice materials.thank a lot
ReplyDeleteGreat
ReplyDeleteI think you should add the index but normal and no add on's but other than that great work.
ReplyDeleteCan you help me with what is found on the periphery of the map,
ReplyDeleteCool and I have a super give: How Much Home Renovation Can I Afford gutting a house
ReplyDeleteThanks so much you have really helped me
ReplyDeletethanks so much this really helped with my tournament!
ReplyDeletethank you
ReplyDeleteslay baddie
ReplyDeletei like it very resourceful
ReplyDeleteVery Goood
ReplyDeleteGreat Job! This seems like it took insane research!
ReplyDeletethanks very helpful.
ReplyDeleteIt was so nice
ReplyDeleteGood keep it up👍
ReplyDeleteMuch Thanks to you
ReplyDeleteGreat work, congrats 👍👍
ReplyDeleteVery goog
ReplyDelete